SCI Publications
2009
E. Jurrus, M. Hardy, T. Tasdizen, P.T. Fletcher, P. Koshevoy, C.-B. Chien, W. Denk, R.T. Whitaker.
“Axon Tracking in Serial Block-Face Scanning Electron Microscopy,” In Medical Image Analysis (MEDIA), Vol. 13, No. 1, Elsevier, pp. 180--188. February, 2009.
PubMed ID: 18617436
E. Jurrus, A.R.C. Paiva, S. Watanabe, R.T. Whitaker, E.M. Jorgensen, T. Tasdizen.
“Serial Neural Network Classifier for Membrane Detection using a Filter Bank.,” SCI Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2009-006, SCI Institute, University of Utah, 2009.
E. Jurrus, A.R.C. Paiva, S. Watanabe, R. Whitaker, E.M. Jorgensen, T. Tasdizen.
“Serial Neural Network Classifier for Membrane Detection using a Filter Bank,” In Proc. Workshop on Microscopic Image Analysis with Applications in Biology, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009.
A. Knoll, I. Wald, C.D. Hansen.
“Coherent Multiresolution Isosurface Ray Tracing,” In The Visual Computer, Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 209--225. 2009.
A. Knoll, Y. Hijazi, C.D. Hansen, I. Wald, H. Hagen.
“Fast Ray Tracing of Arbitrary Implicit Surfaces with Interval and Affine Arithmetic,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 26--40. 2009.
A. Knoll, Y. Hijazi, R. Westerteiger, M. Schott, C.D. Hansen, H. Hagen.
“Volume Ray Casting with Peak Finding and Differential Sampling,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Visualization Conference, Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 1571--1578. Sept/Oct, 2009.
A. Knoll, Y. Hijazi, R. Westerteiger, M. Schott, C.D. Hansen, Hans Hagen.
“Volume Ray Casting with Peak Finding and Differential Sampling,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 1571-1578. 2009.
J. Krüger, T. Fogal.
“Focus and Context - Visualization without the Complexity,” In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, September 7 - 12, 2009, Munich, Germany, IFMBE Proceedings, Vol. 25/13, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 44--48. 2009.
S. Lew, C.H. Wolters, T. Dierkes, C. Röer, R.S. MacLeod.
“Accuracy and run-time comparison for different potential approaches and iterative solvers in finite element method based EEG source analysis,” In Applied Numerical Mathematics, Vol. 59, pp. 1970--1988. 2009.
S. Lew, C.H. Wolters, A. Anwander, S. Makeig, R.S. MacLeod.
“Improved EEG Source Analysis Using Low-Resolution Conductivity Estimation in a Four-Compartment Finite Element Head Model,” In Human Brain Mapping, Vol. 30, pp. 2862--2878. 2009.
J. Li, D. Xiu.
“A Generalized Polynomial Chaos Based Ensemble Kalman Filter with High Accuracy,” In Journal of Computational Physics, Vol. 228, No. 15, pp. 5454--5469. 2009.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2009.04.029
As one of the most adopted sequential data assimilation methods in many areas, especially those involving complex nonlinear dynamics, the ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF) has been under extensive investigation regarding its properties and efficiency. Compared to other variants of the Kalman filter (KF), EnKF is straightforward to implement, as it employs random ensembles to represent solution states. This, however, introduces sampling errors that affect the accuracy of EnKF in a negative manner. Though sampling errors can be easily reduced by using a large number of samples, in practice this is undesirable as each ensemble member is a solution of the system of state equations and can be time consuming to compute for large-scale problems. In this paper we present an efficient EnKF implementation via generalized polynomial chaos (gPC) expansion. The key ingredients of the proposed approach involve (1) solving the system of stochastic state equations via the gPC methodology to gain efficiency; and (2) sampling the gPC approximation of the stochastic solution with an arbitrarily large number of samples, at virtually no additional computational cost, to drastically reduce the sampling errors. The resulting algorithm thus achieves a high accuracy at reduced computational cost, compared to the classical implementations of EnKF. Numerical examples are provided to verify the convergence property and accuracy improvement of the new algorithm. We also prove that for linear systems with Gaussian noise, the first-order gPC Kalman filter method is equivalent to the exact Kalman filter.
Keywords: Kalman filter, Data assimilation, Polynomial chaos, Uncertainty quantification
Z. Liu, H. Zhu, B.L. Marks, L.M. Katz, C.B. Goodlett, G. Gerig, M. Styner.
“Voxel-wise group analysis of DTI,” In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 2009, pp. 807--810. 2009.
DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2009.5193172
J. Luitjens, M. Berzins.
“Uintah: A Scalable Adaptive Framework for Emerging Petascale Platforms,” SCI Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2009-002, SCI Institute, University of Utah, 2009.
S.A. Maas, B.J. Ellis, D.S. Rawlins, J.A. Weiss.
“A Comparison of FEBio, ABAQUS, and NIKE3D Results for a Suite of Verification Problems,” SCI Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2009-009, SCI Institute, University of Utah, 2009.
R.S. MacLeod, J.G. Stinstra, S. Lew, R.T. Whitaker, D.J. Swenson, M.J. Cole, J. Krüger, D.H. Brooks, C.R. Johnson.
“Subject-specific, multiscale simulation of electrophysiology: a software pipeline for image-based models and application examples,” In Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society A, Mathematical, Physical & Engineering Sciences, Vol. 367, No. 1896, pp. 2293--2310. 2009.
C.B. Maks, C.R. Butson, B.L. Walter, J.L. Vitek, C.C. McIntyre.
“Deep brain stimulation activation volumes and their association with neurophysiological mapping and therapeutic outcomes,” In Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, Vol. 80, No. 6, pp. 659--666. June, 2009.
ISSN: 1468-330X
DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2007.126219
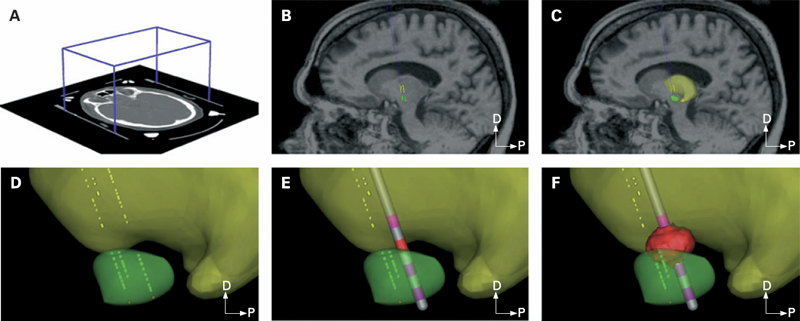
METHODS: Each patient specific model was created with a series of five steps: (1) definition of the neurosurgical stereotactic coordinate system within the context of preoperative imaging data; (2) entry of intraoperative microelectrode recording locations from neurophysiologically defined thalamic, subthalamic and substantia nigra neurons into the context of the imaging data; (3) fitting a three dimensional brain atlas to the neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of the patient; (4) positioning the DBS electrode in the documented stereotactic location, verified by postoperative imaging data; and (5) calculation of the VTA using a diffusion tensor based finite element neurostimulation model.
RESULTS: The patient specific models show that therapeutic benefit was achieved with direct stimulation of a wide range of anatomical structures in the subthalamic region. Interestingly, of the five patients exhibiting a greater than 40\% improvement in their Unified PD Rating Scale (UPDRS), all but one had the majority of their VTA outside the atlas defined borders of the STN. Furthermore, of the five patients with less than 40\% UPDRS improvement, all but one had the majority of their VTA inside the STN.
CONCLUSIONS: Our results are consistent with previous studies suggesting that therapeutic benefit is associated with electrode contacts near the dorsal border of the STN, and provide quantitative estimates of the electrical spread of the stimulation in a clinically relevant context.
Keywords: Brain Mapping, Brain Mapping: methods, Cerebral,Cerebral: physiology, Computer-Assisted, Computer-Assisted: methods, Deep Brain Stimulation, Deep Brain Stimulation: methods, Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging: methods, Dominance, Electrodes, Humans, Image Processing, Imaging, Implanted, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Magnetic Resonance Imaging: methods, Nerve Net, Nerve Net: physiopathology, Neurologic Examination, Neurons, Neurons: physiology, Parkinson Disease, Parkinson Disease: physiopathology, Parkinson Disease: therapy, Substantia Nigra, Substantia Nigra: physiopathology, Subthalamic Nucleus, Subthalamic Nucleus: physiopathology, Synaptic Transmission, Synaptic Transmission: physiology, Thalamus, Thalamus: physiopathology, Three-Dimensional, Tomography, Treatment Outcome, X-Ray Computed, X-Ray Computed: methods
H.G. Martinez, S.I. Prajapati, C.A. Estrada, F. Jimenez, M.P. Quinones, I. Wu, A. Bahadur, A. Sanderson, C.R. Johnson, M. Shim, C. Keller, S.S. Ahuja.
“Microscopic Computed Tomography Based Virtual Histology for Visualization and Morphometry of Atherosclerosis in Diabetic Apolipoprotein E Mutant Mice,” In Circulation: Journal of the American Heart Association, Vol. 120, No. 9, pp. 821--822. 2009.
H. Martinez, S. Prajapati, C. Estrada, F. Jimenez, I. Wu, A. Bahadur, A. Sanderson, C.R. Johnson, M. Shim, C. Keller, S. Ahuja.
“Microscopic Computed Tomography–Based Virtual Histology for Visualization and Morphometry of Atherosclerosis in Diabetic Apolipoprotein E Mutant Mice,” In Circulation, Vol. 120, No. 821--822, 2009.
Y. Marzouk, D. Xiu.
“A Stochastic Collocation Approach to Bayesian Inference in Inverse Problems,” In Communications in Computational Physics, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 826--847. 2009.
DOI: 10.4208/cicp.2009.v6.p826
We present an efficient numerical strategy for the Bayesian solution of inverse problems. Stochastic collocation methods, based on generalized polynomial chaos (gPC), are used to construct a polynomial approximation of the forward solution over the support of the prior distribution. This approximation then defines a surrogate posterior probability density that can be evaluated repeatedly at minimal computational cost. The ability to simulate a large number of samples from the posterior distribution results in very accurate estimates of the inverse solution and its associated uncertainty. Combined with high accuracy of the gPC-based forward solver, the new algorithm can provide great efficiency in practical applications. A rigorous error analysis of the algorithm is conducted, where we establish convergence of the approximate posterior to the true posterior and obtain an estimate of the convergence rate. It is proved that fast (exponential) convergence of the gPC forward solution yields similarly fast (exponential) convergence of the posterior. The numerical strategy and the predicted convergence rates are then demonstrated on nonlinear inverse problems ofvarying smoothness and dimension.
Keywords: Inverse problems, Bayesian inference, stochastic collocation, generalized polynomial
M.D. Meyer, T. Munzner, H. Pfister.
“MizBee: A Multiscale Synteny Browser,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (Proceedings of InfoVis 2009), Vol. 15, No. 6, Note: Honorable Mention for Best Paper Award, pp. 897--904. 2009.
Page 73 of 144
