SCI Publications
2011
S. Philip, B. Summa, P.-T. Bremer, and V. Pascucci.
“Parallel Gradient Domain Processing of Massive Images,” In Proceedings of the 2011 Eurographics Symposium on Parallel Graphics and Visualization, pp. 11--19. 2011.

S. Philip, B. Summa, P-T Bremer, V. Pascucci.
“Hybrid CPU-GPU Solver for Gradient Domain Processing of Massive Images,” In Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), pp. 244--251. 2011.

T.A. Quinn, S. Granite, M.A. Allessie, C. Antzelevitch, C. Bollensdorff, G. Bub, R.A.B. Burton, E. Cerbai, P.S. Chen, M. Delmar, D. DiFrancesco, Y.E. Earm, I.R. Efimov, M. Egger, E. Entcheva, M. Fink, R. Fischmeister, M.R. Franz, A. Garny, W.R. Giles, T. Hannes, S.E. Harding, P.J. Hunter, s, G. Iribe, J. Jalife, C.R. Johnson, R.S. Kass, I. Kodama, G. Koren, P. Lord, V.S. Markhasin, S. Matsuoka, A.D. McCulloch, G.R. Mirams, G.E. Morley, S. Nattel, D. Noble, S.P. Olesen, A.V. Panfilov, N.A. Trayanova, U. Ravens, S. Richard, D.S. Rosenbaum, Y. Rudy, F. Sachs, F.B. Sachse, D.A. Saint, U. Schotten, O. Solovyova, P. Taggart, L. Tung, A. Varrò, P.G. Volders, K. Wang, J.N. Weiss, E. Wettwer, E. White, R. Wilders, R.L. Winslow, P. Kohl.
“Minimum Information about a Cardiac Electrophysiology Experiment (MICEE): Standardised reporting for model reproducibility, interoperability, and data sharing,” In Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, Vol. 107, No. 1, Elsevier, pp. 4--10. October, 2011.
DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.07.001
PubMed Central ID: PMC3190048
Cardiac experimental electrophysiology is in need of a well-defined Minimum Information Standard for recording, annotating, and reporting experimental data. As a step toward establishing this, we present a draft standard, called Minimum Information about a Cardiac Electrophysiology Experiment (MICEE). The ultimate goal is to develop a useful tool for cardiac electrophysiologists which facilitates and improves dissemination of the minimum information necessary for reproduction of cardiac electrophysiology research, allowing for easier comparison and utilisation of findings by others. It is hoped that this will enhance the integration of individual results into experimental, computational, and conceptual models. In its present form, this draft is intended for assessment and development by the research community. We invite the reader to join this effort, and, if deemed productive, implement the Minimum Information about a Cardiac Electrophysiology Experiment standard in their own work.
Keywords: Minimum Information Standard; Cardiac electrophysiology; Data sharing; Reproducibility; Integration; Computational modelling
W. Reich, Dominic Schneider, Christian Heine, Alexander Wiebel, Guoning Chen, Gerik Scheuermann.
“Combinatorial Vector Field Topology in 3 Dimensions,” In Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (MMBIA) Proceedings IEEE MMBIA 2012, pp. 47--59. November, 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-23175-9_4
In this paper, we present two combinatorial methods to process 3-D steady vector fields, which both use graph algorithms to extract features from the underlying vector field. Combinatorial approaches are known to be less sensitive to noise than extracting individual trajectories. Both of the methods are a straightforward extension of an existing 2-D technique to 3-D fields. We observed that the first technique can generate overly coarse results and therefore we present a second method that works using the same concepts but produces more detailed results. We evaluate our method on a CFD-simulation of a gas furnace chamber. Finally, we discuss several possibilities for categorizing the invariant sets with respect to the flow.
P. Rosen, V. Popescu, K. Hayward, C. Wyman.
“Non-Pinhole Approximations for Interactive Rendering,” In IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, Vol. 99, 2011.
P. Rosen, V. Popescu.
“An Evaluation of 3-D Scene Exploration Using a Multiperspective Image Framework,” In The Visual Computer, Vol. 27, No. 6-8, Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., pp. 623--632. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/s00371-011-0599-2
PubMed ID: 22661796
PubMed Central ID: PMC3364594
Multiperspective images (MPIs) show more than what is visible from a single viewpoint and are a promising approach for alleviating the problem of occlusions. We present a comprehensive user study that investigates the effectiveness of MPIs for 3-D scene exploration. A total of 47 subjects performed searching, counting, and spatial orientation tasks using both conventional and multiperspective images. We use a flexible MPI framework that allows trading off disocclusion power for image simplicity. The framework also allows rendering MPI images at interactive rates, which enables investigating interactive navigation and dynamic 3-D scenes. The results of our experiments show that MPIs can greatly outperform conventional images. For searching, subjects performed on average 28% faster using an MPI. For counting, accuracy was on average 91% using MPIs as compared to 42% for conventional images.
Keywords: Interactive 3-D scene exploration, Navigation, Occlusions, User study, Visual interfaces
N. Sadeghi, M.W. Prastawa, P.T. Fletcher, J.H. Gilmore, W. Lin, G. Gerig.
“Statistical Growth Modeling of Longitudinal DT-MRI for Regional Characterization of Early Brain Development,” In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2011 Workshop on Image Analysis of Human Brain Development, pp. 1507--1510. 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2012.6235858
A population growth model that represents the growth trajectories of individual subjects is critical to study and understand neurodevelopment. This paper presents a framework for jointly estimating and modeling individual and population growth trajectories, and determining significant regional differences in growth pattern characteristics applied to longitudinal neuroimaging data. We use non-linear mixed effect modeling where temporal change is modeled by the Gompertz function. The Gompertz function uses intuitive parameters related to delay, rate of change, and expected asymptotic value; all descriptive measures which can answer clinical questions related to growth. Our proposed framework combines nonlinear modeling of individual trajectories, population analysis, and testing for regional differences. We apply this framework to the study of early maturation in white matter regions as measured with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Regional differences between anatomical regions of interest that are known to mature differently are analyzed and quantified. Experiments with image data from a large ongoing clinical study show that our framework provides descriptive, quantitative information on growth trajectories that can be directly interpreted by clinicians. To our knowledge, this is the first longitudinal analysis of growth functions to explain the trajectory of early brain maturation as it is represented in DTI.
Keywords: namic
B. Salter, B. Wang, M. Sadinski, S. Ruhnau, V. Sarkar, J. Hinkle, Y. Hitchcock, K. Kokeny, S. Joshi.
“WE-E-BRC-06: Comparison of Two Methods of Contouring Internal Target Volume on Multiple 4DCT Data Sets from the Same Subjects: Maximum Intensity Projection and Combination of 10 Phases,” In Medical Physics, Vol. 38, No. 6, pp. 3820. 2011.
R. Samuel, H.J. Sant, F. Jiao, C.R. Johnson, B.K. Gale.
“Microfluidic laminate-based phantom for diffusion tensor-magnetic resonance imaging,” In Journal of Micromech. Microeng., Vol. 21, pp. 095027--095038. 2011.
DOI: 10.1088/0960-1317/21/9/095027
M. Schott, A.V.P. Grosset, T. Martin, V. Pegoraro, S.T. Smith, C.D. Hansen.
“Depth of Field Effects for Interactive Direct Volume Rendering,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 30, No. 3, Edited by H. Hauser and H. Pfister and J.J. van Wijk, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 941--950. jun, 2011.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2011.01943.x
M. Schulz, J.A. Levine, P.-T. Bremer, T. Gamblin, V. Pascucci.
“Interpreting Performance Data Across Intuitive Domains,” In International Conference on Parallel Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, IEEE, pp. 206--215. 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/ICPP.2011.60
M. Seyedhosseini, A.R.C. Paiva, T. Tasdizen.
“Multi-scale Series Contextual Model for Image Parsing,” SCI Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2011-004, SCI Institute, University of Utah, 2011.
M. Seyedhosseini, A.R.C. Paiva, T. Tasdizen.
“Fast AdaBoost training using weighted novelty selection,” In Proc. IEEE Intl. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, San Jose, CA, USA pp. 1245--1250. August, 2011.
In this paper, a new AdaBoost learning framework, called WNS-AdaBoost, is proposed for training discriminative models. The proposed approach significantly speeds up the learning process of adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) by reducing the number of data points. For this purpose, we introduce the weighted novelty selection (WNS) sampling strategy and combine it with AdaBoost to obtain an efficient and fast learning algorithm. WNS selects a representative subset of data thereby reducing the number of data points onto which AdaBoost is applied. In addition, WNS associates a weight with each selected data point such that the weighted subset approximates the distribution of all the training data. This ensures that AdaBoost can trained efficiently and with minimal loss of accuracy. The performance of WNS-AdaBoost is first demonstrated in a classification task. Then, WNS is employed in a probabilistic boosting-tree (PBT) structure for image segmentation. Results in these two applications show that the training time using WNS-AdaBoost is greatly reduced at the cost of only a few percent in accuracy.
M. Seyedhosseini, R. Kumar, E. Jurrus, R. Guily, M. Ellisman, H. Pfister, T. Tasdizen.
“Detection of Neuron Membranes in Electron Microscopy Images using Multi-scale Context and Radon-like Features,” In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2011, Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 6891, pp. 670--677. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-23623-5_84
F. Shi, D. Shen, P.-T. Yap, Y. Fan, J.-Z. Cheng, H. An, L.L. Wald, G. Gerig, J.H. Gilmore, W. Lin.
“CENTS: Cortical Enhanced Neonatal Tissue Segmentation,” In Human Brain Mapping HBM, Vol. 32, No. 3, Note: ePub 5 Aug 2010, pp. 382--396. March, 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21023
PubMed ID: 20690143
M. Steinberger, M. Waldner, M. Streit, A. Lex, D. Schmalstieg.
“Context-Preserving Visual Links,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (InfoVis '11), Vol. 17, No. 12, 2011.
Evaluating, comparing, and interpreting related pieces of information are tasks that are commonly performed during visual data analysis and in many kinds of information-intensive work. Synchronized visual highlighting of related elements is a well-known technique used to assist this task. An alternative approach, which is more invasive but also more expressive is visual linking in which line connections are rendered between related elements. In this work, we present context-preserving visual links as a new method for generating visual links. The method specifically aims to fulfill the following two goals: first, visual links should minimize the occlusion of important information; second, links should visually stand out from surrounding information by minimizing visual interference. We employ an image-based analysis of visual saliency to determine the important regions in the original representation. A consequence of the image-based approach is that our technique is application-independent and can be employed in a large number of visual data analysis scenarios in which the underlying content cannot or should not be altered. We conducted a controlled experiment that indicates that users can find linked elements in complex visualizations more quickly and with greater subjective satisfaction than in complex visualizations in which plain highlighting is used. Context-preserving visual links were perceived as visually more attractive than traditional visual links that do not account for the context information.
B. Summa, G. Scorzelli, M. Jiang, P.-T. Bremer, V. Pascucci.
“Interactive Editing of Massive Imagery Made Simple: Turning Atlanta into Atlantis,” In ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 7:1--7:13. April, 2011.
DOI: 10.1145/1944846.1944847
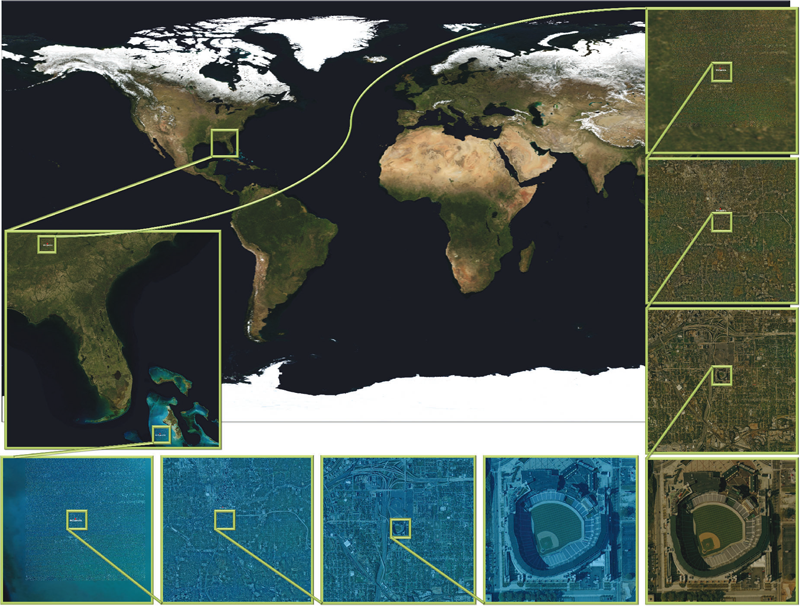
This article presents a simple framework for progressive processing of high-resolution images with minimal resources. We demonstrate this framework's effectiveness by implementing an adaptive, multi-resolution solver for gradient-based image processing that, for the first time, is capable of handling gigapixel imagery in real time. With our system, artists can use commodity hardware to interactively edit massive imagery and apply complex operators, such as seamless cloning, panorama stitching, and tone mapping.
We introduce a progressive Poisson solver that processes images in a purely coarse-to-fine manner, providing near instantaneous global approximations for interactive display (see Figure 1). We also allow for data-driven adaptive refinements to locally emulate the effects of a global solution. These techniques, combined with a fast, cache-friendly data access mechanism, allow the user to interactively explore and edit massive imagery, with the illusion of having a full solution at hand. In particular, we demonstrate the interactive modification of gigapixel panoramas that previously required extensive offline processing. Even with massive satellite images surpassing a hundred gigapixels in size, we enable repeated interactive editing in a dynamically changing environment. Images at these scales are significantly beyond the purview of previous methods yet are processed interactively using our techniques. Finally our system provides a robust and scalable out-of-core solver that consistently offers high-quality solutions while maintaining strict control over system resources.
D.J. Swenson, S.E. Geneser, J.G. Stinstra, R.M. Kirby, R.S. MacLeod.
“Cardiac Position Sensitivity Study in the Electrocardiographic Forward Problem Using Stochastic Collocation and Boundary Element Methods,” In Annals of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. 12, pp. 2900--2910. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/s10439-011-0391-5
PubMed ID: 21909818
PubMed Central ID: PMC336204
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is ubiquitously employed as a diagnostic and monitoring tool for patients experiencing cardiac distress and/or disease. It is widely known that changes in heart position resulting from, for example, posture of the patient (sitting, standing, lying) and respiration significantly affect the body-surface potentials; however, few studies have quantitatively and systematically evaluated the effects of heart displacement on the ECG. The goal of this study was to evaluate the impact of positional changes of the heart on the ECG in the specific clinical setting of myocardial ischemia. To carry out the necessary comprehensive sensitivity analysis, we applied a relatively novel and highly efficient statistical approach, the generalized polynomial chaos-stochastic collocation method, to a boundary element formulation of the electrocardiographic forward problem, and we drove these simulations with measured epicardial potentials from whole-heart experiments. Results of the analysis identified regions on the body-surface where the potentials were especially sensitive to realistic heart motion. The standard deviation (STD) of ST-segment voltage changes caused by the apex of a normal heart, swinging forward and backward or side-to-side was approximately 0.2 mV. Variations were even larger, 0.3 mV, for a heart exhibiting elevated ischemic potentials. These variations could be large enough to mask or to mimic signs of ischemia in the ECG. Our results suggest possible modifications to ECG protocols that could reduce the diagnostic error related to postural changes in patients possibly suffering from myocardial ischemia.
M. Szegedi, J. Hinkle, S. Joshi, V. Sarkar, P. Rassiah-Szegedi, B. Wang, B. Salter.
“WE-E-BRC-05: Voxel Based Four Dimensional Tissue Deformation Reconstruction (4DTDR) Validation Using a Real Tissue Phantom,” In Medical Physics, Vol. 38, pp. 3819. 2011.
G. Tamm, A. Schiewe, J. Krüger.
“ZAPP – A management framework for distributed visualization systems,” In Proceedings of CGVCVIP 2011 : IADIS International Conference on Computer Graphics, Visualization, Computer Vision And Image Processing, pp. (accepted). 2011.
Page 63 of 144
