SCI Publications
2011
C.D. Cantwell, S.J. Sherwin, R.M. Kirby, P.H.J. Kelly.
“From h to p Efficiently: Selecting the Optimal Spectral/hp Discretisation in Three Dimensions,” In Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 84--96. 2011.
G. Chen, D. Palke, Z. Lin, H. Yeh, P. Vincent, R.S. Laramee, E. Zhang.
“Asymmetric Tensor Field Visualization for Surfaces,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 17, No. 12, IEEE, pp. 1979-1988. Dec, 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/tvcg.2011.170
Guoning Chen, Qingqing Deng, Andrzej Szymczak, Robert S. Laramee, and Eugene Zhang.
“Morse Set Classification and Hierarchical Refinement using Conley Index,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), Vol. 18, No. 5, pp. 767--782. June, 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2011.107
PubMed ID: 21690641
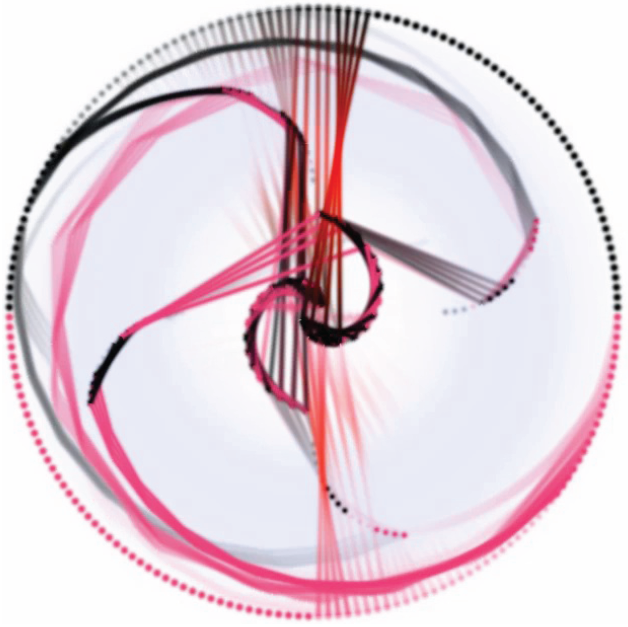
Morse decomposition provides a numerically stable topological representation of vector fields that is crucial for their rigorous interpretation. However, Morse decomposition is not unique, and its granularity directly impacts its computational cost. In this paper, we propose an automatic refinement scheme to construct the Morse Connection Graph (MCG) of a given vector field in a hierarchical fashion. Our framework allows a Morse set to be refined through a local update of the flow combinatorialization graph, as well as the connection regions between Morse sets. The computation is fast because the most expensive computation is concentrated on a small portion of the domain. Furthermore, the present work allows the generation of a topologically consistent hierarchy of MCGs, which cannot be obtained using a global method. The classification of the extracted Morse sets is a crucial step for the construction of the MCG, for which the Poincaré index is inadequate. We make use of an upper bound for the Conley index, provided by the Betti numbers of an index pair for a translation along the flow, to classify the Morse sets. This upper bound is sufficiently accurate for Morse set classification and provides supportive information for the automatic refinement process. An improved visualization technique for MCG is developed to incorporate the Conley indices. Finally, we apply the proposed techniques to a number of synthetic and real-world simulation data to demonstrate their utility.
A.N.M. Imroz Choudhury, P. Rosen.
“Abstract Visualization of Runtime Memory Behavior,” In 6th IEEE International Workshop on Visualizing Software for Understanding and Analysis (VISSOFT 2011), pp. 22--29. 2011.

A. Cuadros-Vargas, L.G. Nonato, V. Pascucci.
“Combinatorial Laplacian Image Cloning,” In Proceedings of XXIV Sibgrapi – Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images, pp. 236--241. 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/SIBGRAPI.2011.7
Seamless image cloning has become one of the most important editing operation for photomontage. Recent coordinate-based methods have lessened considerably the computational cost of image cloning, thus enabling interactive applications. However, those techniques still bear severe limitations as to concavities and dynamic shape deformation. In this paper we present novel methodology for image cloning that turns out to be highly efficient in terms of computational times while still being more flexible than existing techniques. Our approach builds on combinatorial Laplacian and fast Cholesky factorization to ensure interactive image manipulation, handling holes, concavities, and dynamic deformations during the cloning process. The provided experimental results show that the proposed technique outperforms existing methods in requisites such as accuracy and flexibility.
M. Daccarett, T.J. Badger, N. Akoum, N.S. Burgon, C. Mahnkopf, G.R. Vergara, E.G. Kholmovski, C.J. McGann, D.L. Parker, J. Brachmann, R.S. Macleod, N.F. Marrouche.
“Association of left atrial fibrosis detected by delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging and the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation,” In Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Vol. 57, No. 7, pp. 831--838. 2011.
PubMed ID: 21310320
M. Daccarett, C.J. McGann, N.W. Akoum, R.S. MacLeod, N.F. Marrouche.
“MRI of the left atrium: predicting clinical outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation,” In Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 105--111. 2011.
PubMed ID: 21166532
M. Datar, Y. Gur, B. Paniagua, M. Styner, R.T. Whitaker.
“Geometric Correspondence for Ensembles of Nonregular Shapes,” In Proceedings of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2011), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 6892, pp. 368--375. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-23629-7_45
PubMed ID: 21995050
PubMed Central ID: PMC3346950
Keywords: namic
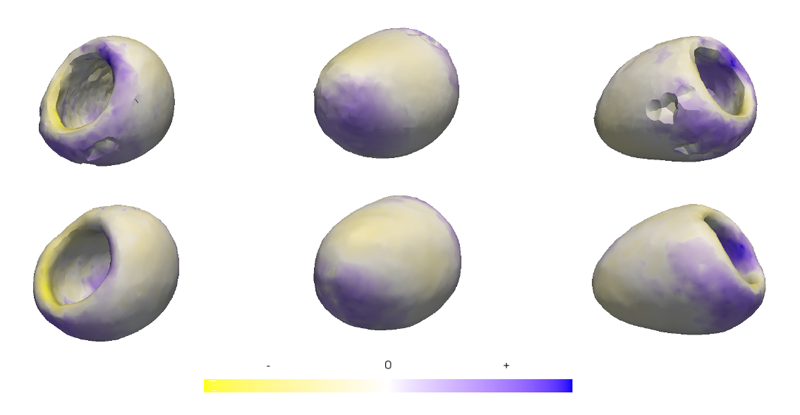
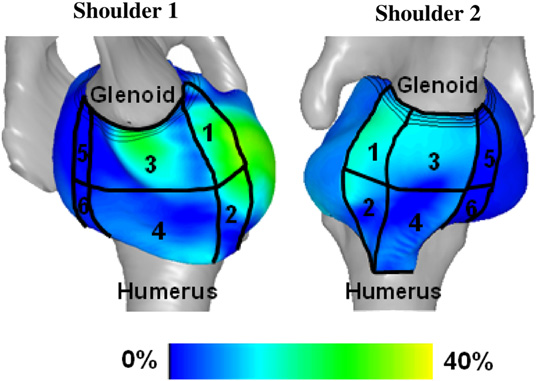
N.J. Drury, B.J. Ellis, J.A. Weiss, P.J. McMahon, R.E. Debski.
“Finding consistent strain distributions in the glenohumeral capsule between two subjects: Implications for development of physical examinations,” In Journal of Biomechanics, Vol. 44, No. 4, pp. 607-613. February, 2011.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.11.018
S. Durrleman, M.W. Prastawa, G. Gerig, S. Joshi.
“Optimal data-driven sparse parameterization of diffeomorphisms for population analysis,” In Proceedings of the IPMI 2011 conference, Springer LNCS, Vol. 6801/2011, pp. 123--134. July, 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-22092-0_11
PubMed ID: 20516153
S. Durrleman, X. Pennec, A. Trouvé, N. Ayache, J. Braga.
“Comparison of the endocranial ontogenies between chimpanzees and bonobos via temporal regression and spatiotemporal registration,” In Journal of Human Evolution, pp. 74--88. January, 2011.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.10.004
PubMed ID: 22137587
This paper aims at quantifying ontogenetic differences between bonobo (Pan paniscus) and chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) endocrania, using dental development as a timeline. We utilize a methodology based on smooth and invertible deformations combined with a metric of "currents" that defines a distance between endocranial surfaces and does not rely on correspondence between landmarks. This allows us to perform a temporal surface regression that estimates typical endocranial ontogenetic trajectories separately for bonobos and chimpanzees. We highlight non-linear patterns of endocranial ontogenetic change and significant differences between species at local anatomical levels rather than considering the endocranium as a uniform entity. A spatiotemporal registration permits the quantification of inter-species differences decomposed into a morphological deformation (accounting for size and shape differences independently of age) and a time warp (accounting for changes in the dynamics of development). Our statistical simulations suggest that patterns of endocranial volume (EV) increase may differ significantly between bonobos and chimpanzees, with an earlier phase of a relatively rapid increase (preferentially at some endocranial subdivisions) in the former and a much later phase of relatively rapid increase in the latter. As a consequence, the chimpanzee endocranium appears to reach its adult size later. Moreover, the time warp indicates that juvenile bonobos develop much slower than juvenile chimpanzees, suggesting that inter-specific ontogenetic shifts do not only concern EV increase, but also the rate of shape changes over time. Our method provides, for the first time, a quantitative estimation of inter-specific ontogenetic shifts that appear to differentiate non-linearly.
M. Edmunds, T. McLoughlin, R.S. Laramee, G. Chen, E. Zhang, N. Max.
“Automatic Stream Surface Seeding,” In EUROGRAPHICS 2011 Short Papers, pp. 53--56. 2011.
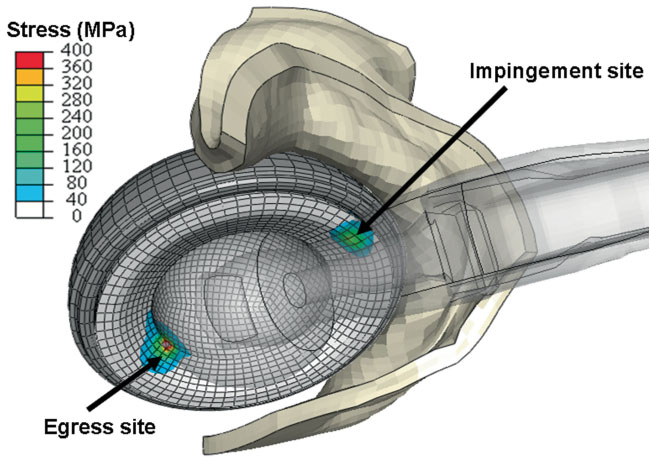
J.M. Elkins, J.S. Stroud, M.J. Rudert, Y. Tochigi, D.R. Pedersen, B.J. Ellis, J.J. Callaghan, J.A. Weiss, T.D. Brown.
“The capsule's contribution to total hip construct stability - a finite element analysis,” In Journal of Orthopedic Research, Vol. 29, No. 11, Note: William Harris, MD Award, pp. 1642--1648. November, 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/jor.21435
B.J. Ellis.
“Finite element modeling of knee and shoulder ligaments,” Note: Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Bioengineering, University of Utah, 2011.
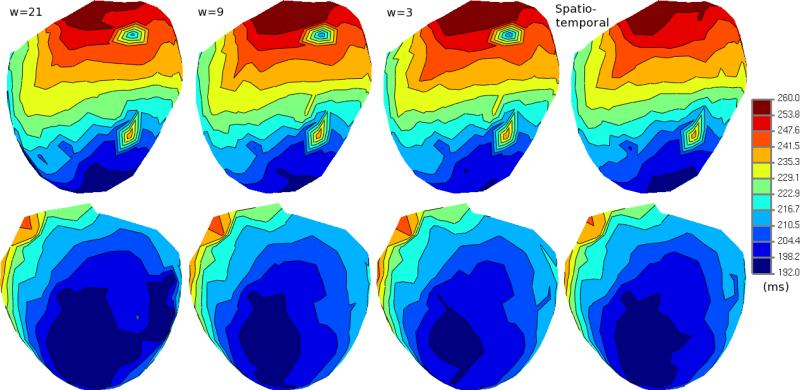
B. Erem, D.H. Brooks, P.M. van Dam, J.G. Stinstra, R.S. MacLeod.
“Spatiotemporal Estimation of Activation Times of Fractionated ECGs on Complex Heart Surfaces,” In Proceedings of the International Coference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), pp. 5884--5887. 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6091455
PubMed ID: 22255678
PubMed Central ID: PMC3345888
T. Etiene, L.G. Nonato, C. Scheidegger, J. Tierny, T.J. Peters, V. Pascucci, R.M. Kirby, C.T. Silva.
“Topology Verfication for Isosurface Extraction,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, pp. (accepted). 2011.
J. Fishbaugh, S. Durrleman, G. Gerig.
“Estimation of Smooth Growth Trajectories with Controlled Acceleration from Time Series Shape Data,” In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, LNCS 6892, Springer, pp. 401--408. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-23629-7_49
Longitudinal shape analysis often relies on the estimation of a realistic continuous growth scenario from data sparsely distributed in time. In this paper, we propose a new type of growth model parameterized by acceleration, whereas standard methods typically control the velocity. This mimics the behavior of biological tissue as a mechanical system driven by external forces. The growth trajectories are estimated as smooth flows of deformations, which are twice differentiable. This differs from piecewise geodesic regression, for which the velocity may be discontinuous. We evaluate our approach on a set of anatomical structures of the same subject, scanned 16 times between 4 and 8 years of age. We show our acceleration based method estimates smooth growth, demonstrating improved regularity compared to piecewise geodesic regression. Leave-several-out experiments show that our method is robust to missing observations, as well as being less sensitive to noise, and is therefore more likely to capture the underlying biological growth.
Keywords: na-mic
P.T. Fletcher.
“Geodesic Regression on Riemannian Manifolds,” In Proceedings of the Third MICCIA International Workshop on Mathematical Foundations of Computational Anatomy (MFCA), Toronto, Canada, pp. 75--86. 2011.
P.T. Fletcher, J. Moeller, J. Phillips, S. Venkatasubramanian.
“Horoball hulls and extents in positive definite space,” In Algorithms and Data Structures, Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 6844/2011, pp. 386--398. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-22300-6_33
T. Fogal, J. Krüger.
“Efficient I/O for Parallel Visualization,” In Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Parallel Graphics and Visualization (2011), Edited by T. Kuhlen and R. Pajarola and K. Zhou, pp. 81--90. 2011.
Page 59 of 144
